
India Weekly Watch: 8th September 2025
India’s new GST regime significantly lowers the tax burden on consumers but raises concerns over whether the slash in rates impact the government’s revenue and fiscal deficit target.
Report
B2K Weekly Watch: 1st September 2025
Despite the mixed signals from major high frequency indicators impacted by the early monsoon and tariff woes, the GDP growth far exceeded market expectations and RBI’s estimates of 6.5% in Q1 FY2026.
Report
GDP and GVA overview: Q1 FY2026
Real GDP grew at 7.8% in Q1 FY2026, far above the RBI's estimate of 6.5% due to significant growth in services.
Report
Index of Industrial production: July 2025
IIP growth rose to a four-month high of 3.47% YoY, driven by higher growth in the Manufacturing sector.
Report
India Weekly Watch 25th August 2025
Indian market sentiment remained positive last week, supported by the proposed restructuring of GST reforms and S&P Global’s upgrade of India’s sovereign credit rating, even as lingering global uncertainties continued to weigh on investor confidence.
Report
Index of Eight Core Industries: July 2025
Growth in the Index of Eight Core Industries (ICI) moderated to 2.0% in June 2025 driven by contraction in four out of eight core sectors. Steady growth in Government capital expenditure and infrastructure projects continue to serve as a driver for core industries.
Report
Weekly Watch: 18th August 2025
Indian markets recovered slightly last week breaking their six-week losing streak, buoyed by an upgrade in India’s sovereign credit rating from BBB- to BBB by S&P Global.
Report
WPI: July 2025
WPI inflation rate has declined for the seventh consecutive month to -0.58% on a YoY basis, reaching its lowest level since July 2023. Falling food and fuel prices drove the decline with key items being OTP (Onion, Tomato, Potato) and Crude Petroleum.
Report
CPI July 2025
CPI inflation moderated for the ninth straight month to 1.55% in July driven by falling food prices and a high base effect.
Report
India Weekly Watch: 8th August 2025
The new US tariffs will cause significant short-term losses for Indian exporters as they cannot easily find new buyers immediately.
Report
India Weekly Watch: 2nd August 2025
The Indian markets fell last week and the NSE Nifty 50 marked 5 weeks straight decline, as investor sentiment remained weak on the backdrop of trade uncertainties with the US and discouraging IIP growth numbers.
Report
Index of Industrial Production – June 2025
Index of Industrial Production (IIP) growth moderated for the third consecutive month in June to 1.52%, the lowest level since August 2024, despite improvement in manufacturing sector. Out of 407 item groups in IIP, 211 items recorded negative growth (YoY) suggesting a broad-based weakness in industrial activities.
Report
India Weekly Watch: 26th July 2025
The India-UK trade deal is expected to boost trade between the two country for the next few years. On the domestic front, lack of any major cues from domestic and global front will make it unlikely for Indian markets to make any major shifts.
Report
Index of Eight Core Industries: June 2025
Growth in the overall index in June 2025 improved slightly compared to May 2025, while moderated compared to June 2024. Out of the eight sectors, five experienced contraction in YoY growth.
Report
Weekly Watch-19th July 2025
Inflation fell to its lowest level since January 2019, driven by low food and fuel prices. The rupee depreciated further amidst persistent dollar demand from private and foreign banks.
Report
CPI Inflation Trends: June 2025
Headline inflation fell to its lowest level since January 2019, driven by negative food inflation.
Report
WPI Inflation Trends June 2025
WPI inflation recorded negative growth in June 2025 for the first time since October 2023 driven by deflation in Primary Articles and Fuel and Power.
Report
India Weekly Watch: 12th July 2025
Bank credit growth moderated despite a rate cut by RBI and excess liquidity in the banking system. The rupee weakened amid global uncertainty following Trump’s tariff letters.
Report
8 Years of GST
The GST regime has just reached 8 years of operation as July 1st , 2025. Since it's rollout, it has significantly expanded the taxpayer base leading to a boost in tax collection.
Report
India Weekly Watch 5th July 2025
Manufacturing and services sectors exhibited improved activities in June. Strong demand, especially from international markets led to expansion in manufacturing output, new orders and job creation.
Report
Index of Industrial Production: May 2025
The Index of Industrial Production (IIP) showed moderation in growth in May 2025 and plummeted to it’s lowest in 9 months, 1.23%.
Report
India Weekly Watch:28th June 2025
Following the announcement of the Israel-Iran ceasefire, crude oil prices have declined sharply, providing comfort to India’s external trade.
Report
India Weekly Watch: 21st June 2025
Disinflation in vegetables, condiments and spices, pulses crude petroleum and natural gas led to a sharp fall in WPI inflation. Infrastructure output moderated to 0.7% YoY driven by the poor performance of crude oil, natural gas, fertilizer and electricity sectors.
Report
Index of Eight Core Industries May 2025
Growth of Overall Index once again moderated in May 2025 following heightened global tension and uncertainty
Report
WPI Inflation Trends: May 2025
WPI Inflation rate fell to a one-year low of 0.39% in May 2025 driven by disinflation in Primary Articles and Fuel and Power.
Report
India Weekly Watch 14th June 2025
Retail inflation fell to it's lowest level in May since February 2019 driven by a sharp fall in food prices. However core inflation rose slightly higher in May.
Report
B2K Economy Bytes - CPI Inflation Trends May 2025
CPI inflation fell to its lowest level in six years in May 2025, primarily due to a sharp decline in food inflation. Core inflation edged up slightly, while fuel inflation eased marginally. The outlook remains benign and aligns with the RBI’s projections.
Report
India Weekly Watch: 7th June 2025
The MPC front-loaded rate cuts in June and plan to cut the CRR by a 100 bps in 4 equal tranches to spur demand and economic growth.
Report
MPC Meeting: June 2025
The MPC have front-loaded the rate cuts and reduced the repo rate by 50 bps to 5.50% to support domestic demand.
Report
India Weekly Watch: 30th May 2025
FDI rose to a three-year high of USD 81 billion for FY2025 suggesting strong confidence of foreign investors in Indian markets.
Report
India Weekly Watch: 26th May 2025
RBI has announced the highest-ever dividend transfer of Rs 2.69 lakh crore to the Central Government for FY2025. Additionally, according to official IMF data, India has overtaken Japan to become the fourth largest economy in the world.
Report
India Weekly Watch: 17th May 2025
CPI inflation softened further, boosting hope for a rate cut in the June MPC meeting. The ceasefire announcement between India and Pakistan supported market outlook with positive investor sentiment.
Report
TARIFF TURMOIL: THE US-CHINA TRADE FALLOUT
The Trump administration's tariff war has created turmoil and uncertainty in the global markets. The United States has imposed the highest tariffs on China with tariff rates going up to 245%. China is one of its largest trading partners. China has responded with significantly high tariffs of its own, currently placing rates of 125% on all US imports. The trade relationship between the two countries has deteriorated significantly which places India in a precarious position. The US and China are India's two largest trading partners with India importing the most from China and exporting the most to US. This trade war between the two countries could either be a significant opportunity for India or cost considerable pain.
Report
RBI MPC Meeting: A Dovish Policy Guidance
The Reserve Bank of India’s Monetary Policy Committee (MPC) decided to cut the repo rate by 25 basis points (bps), on 9th April 2025, bringing it down to 6%. Additionally, the policy stance was shifted from neutral to accommodative. These measures aim to address the challenges posed by uncertain global economic conditions, which could hinder the already slowing domestic economic growth. The accommodative stance and rate cut are expected to support the economy by stimulating demand and investments.
Report
India Retail sector -A Tug of war for growth and Profitability
India’s retail sector is $1 trillion market and ranks 5th globally. The sector is moving towards to become a $2 trillion market by 2030, driving to significant shift from unorganised market to organised market. The retail industry landscape is changing in terms of consumer behaviour, technological changes and mode of operation. There is severe competition among modern retailers and the emergence of Q-commerce is further intensifying this competition impacting growth and profitability. E-commerce players are showing high growth but facing challenges in achieving profitability. Q-commerce too are witnessing steep losses despite strong sales growth.
Report
Trump’s Tariff Thump
Trump has stated that the new tariffs will persist until the trade discrepancies between the US and it’s trading partners disappear. His aim is to reduce trade deficits with other countries.US accounts only about 6% of India’s total imports and 18% of total exports. In FY2024, India had a trade surplus of $35 billion.
Report
From Strength to Strength: India’s Fisheries Sector Surges Ahead
In a significant stride of sustainable economic growth, the Indian fisheries sector is making remarkable advancements that will reshape the industry. It is the 3rd largest producer of fishes in the world and contributes nearly 8% to the total production globally. The sector contributes overall 1.1% to the country’s GVA and 6.72% to agriculture GVA of India. With outstanding 8% annual growth rate since 2014 and 10.34% annual growth in FY 22, the fisheries sector is one of the definite cornerstones of India’s economic growth to being a USD 5 trillion economy.
Report
Pharma sector: Riding on an aspirational growth path
India’s pharmaceutical industry continues to be a key player in the global pharmaceutical market and has experienced a significant growth over the years. The total operating revenue has increased from Rs 4,766 crore in FY91 to Rs 449,694 crores in FY22. The Indian pharmaceutical market has witnessed consistent growth due to increasing population, rising middle class income and improved healthcare infrastructure. The market is projected to expand further, driven by the factors such as an aging population, increasing incidence of lifestyle diseases and the growing demand for generic drugs, both in domestic and international market.
Report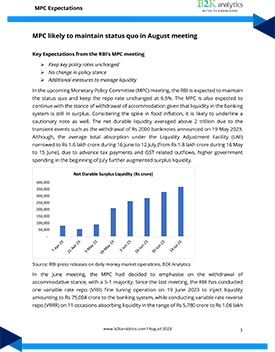
MPC likely to maintain status quo in August meeting
In the upcoming Monetary Policy Committee (MPC) meeting, the RBI is expected to maintain the status quo and keep the repo rate unchanged at 6.5%. The MPC is also expected to continue with the stance of withdrawal of accommodation given that liquidity in the banking system is still in surplus. Considering the spike in food inflation, it is likely to underline a cautionary note as well. The net durable liquidity averaged above 2 trillion due to the transient events such as the withdrawal of Rs 2000 banknotes announced on 19 May 2023.
Report
The Debt Dilemma: Saving the Burden on the Future Generation
Elevated levels of India’s fiscal deficit and public debt have been a matter of concern in India for a long time. Even before the pandemic, debt levels were among the highest in the developing world and emerging market economies. The pandemic pushed the envelope further and relative to the GDP, the fiscal deficit in FY21 increased to 13.3% and the aggregate public debt to 89.6%.
Report
Automobile Industry: Driving the Growth Agenda
The automobile industry is one of the major industries that has expanded rapidly over the reform periods in India. India is one of the biggest automobile manufacturers in the world and has emerged as one of the major contributors to India’s economy. The auto sector contributes nearly 7% to India’s GDP (FY22) and occupies 49% of the manufacturing GDP. The industry is the major contributor of GST to the government as well and provides employment to four and a half crore people in India.
Report
Status Quo on Policy Rates
The Monetary Policy Committee (MPC) of the Reserve Bank of India (RBI), unanimously decided to pause and keep the policy repo rate unchanged at 6.5% in today’s announcement. Also, the MPC decided to emphasise on the withdrawal of accommodative stance, with a 5-1 majority. The decisions are in conformity with our expectations.
Report
MPC likely to pause in the June Meeting
A better-than-expected FY23 GDP data released by the government on 31 May 2023 has renewed the optimism about India’s promising growth recovery. Since the April Monetary Policy Committee (MPC) meeting, the domestic economic conditions have continued to remain resilient, despite the global banking crises and their fallout on global economic environment. Sustaining the quickening of momentum seen in the last few months in FY23, the PMIs in both manufacturing and services have shown creditable expansion in the first two months of FY24. Added to this, CPI inflation eased below 5% in April 2023, for the first time since November 2021.
Report
Sugar Industry Is Not So Sugary: B2K Analytics
The sugar industry witnessed a watershed moment in Sugar Season (SS) 2021-22, with India becoming the world’s second-largest exporter of cane sugar. From a financially distressed sector in 2017-18, the Indian sugar industry was transformed into a state of self-sufficiency, breaking records in sugarcane and sugar production. This outcome was not accidental but predominantly due to a supportive ecosystem provided by collaborative efforts, timely interventions, and governmental policies.
Report
MPC Pauses; No change in policy rates and stance
The Monetary Policy Committee (MPC) of the Reserve Bank of India (RBI), unanimously decided to keep the policy repo rate unchanged at 6.5% in today’s announcement. The calibrated withdrawal of accommodation stance of the MPC continues to remain unchanged, with a 5-1 majority. Today’s policy decision by MPC comes as a bit of a surprise as the market expected a 25-bps rate hike.
Report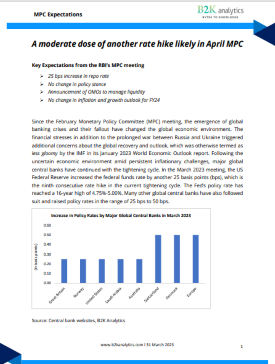
A moderate dose of another rate hike likely in April MPC
Since the February Monetary Policy Committee (MPC) meeting, the emergence of global banking crises and their fallout have changed the global economic environment. The financial stresses in addition to the prolonged war between Russia and Ukraine triggered additional concerns about the global recovery and outlook, which was otherwise termed as less gloomy by the IMF in its January 2023 World Economic Outlook report.
Report
Fiscal Policy Stance is Clearer: On to the Monetary Policy
There were considerable apprehensions about how the Finance Minister would balance the fiscal consolidation objective with the objective of reviving growth by increasing infrastructure spending. The budget proposes to compress the fiscal deficit by half a percentage point to GDP to 5.9% while increasing the capital expenditure from 2.7% of GDP to 3.3%. In nominal terms, this is 37% higher than the revised estimate of the previous year and comes on the back of 23% higher outlay than the revised estimate of the previous year and 39% increase in the year before.
Report
No Indications of Pause; Inflation Precedes Growth
The Monetary Policy Committee (MPC) of the Reserve Bank of India (RBI), in a 4-2 majority decided to increase the policy repo rate by 25 basis points to 6.5% with immediate effect. The calibrated withdrawal of accommodation stance of the MPC continues to remain unchanged, with 4-2 majority. Today’s rate hike decision by MPC is in line with B2K Analytics expectations. This is the sixth straight hike in the policy rate by RBI, and cumulatively the rates have been increased by 250 bps since May 2022, taking the repo rate to the August 2018 level.
Report
Growth - Inflation Dilemma: Modest hike in policy rates by RBI likely
TThe balancing act of supporting growth and controlling inflation remains a priority for RBI’s MPC. After going through successive shocks such as Covid pandemic, lockdowns and geopolitical crises, the domestic economy is expected to grow at a rate of 7% in the current fiscal (FY23). This growth is lower than the 8.7% reported in the previous fiscal (FY22).
Report
Union Budget 2023-24 - Brief Impact Analysis
The total size of the FY24 Budget has increased by 7.5% to Rs 45.03 lakh crore over FY23 revised estimates. Capital expenditure is estimated to increase by a whopping 37.4% in FY24, whereas revenue expenditure is estimated to increase by just 1.3%.
Report
The Inflation-Growth Dilemma: Walking the Tight Rope
This is budget time again and speculations are rife and expectations galore. Although the economy is in a recovery phase, the global headwinds of slowdown, inflation and recession, and continued risks of the virus in countries like China, pose serious policy challenges. In India, the government is faced with the dilemma of having to loosen the purse to fast-paced infrastructure spending to aid growth recovery while containing the fiscal deficit to return to the fiscal consolidation path. This is the last full year before the general elections to the Lok Sabha. Although as many as nine states will go for elections this year, they are unlikely to influence the budget process much.
Report
Impact of Covid 19 on the Uttar Pradesh Handloom Industry A case study by B2K Analytics
This report “The Impact of COVID-19 Pandemic on the Handloom Industry of Uttar Pradesh” is prepared keeping in view the special role of the handloom industry through its contribution to employment generation and foreign exchange earnings in the state’s economy.
Report
Impact of Covid 19 on the Tamil Nadu School System A case study by B2K Analytics
COVID-19 has wreaked havoc on many countries. Governments of fourteen countries have ordered school closures affecting more than 168 million school children. One in seven children have missed more than a tri-quarter of in-person classes, according to UNICEF.
Report
A Glimpse into the Textile Cluster of Tirupur A case study by B2K Analytics
The objective of this report is to provide an insight on Tirupur Textile Industry. From academic researchers to financial analysts, from policy makers to small and big entrepreneurs, Tirupur attracts them all alike.
Report
Automobile firms to require Rs 3.5 lakh crore capital expenditure to realise government’s EV Vision 2030 says B2K Analytics
The impact of Covid-19 on businesses is unprecedented, and the severity of the lockdown and challenges faced by the domestic economy have been starkly brought out by the 23.9% contraction in the GDP in Q1FY 21. Among sectors
Report